1. The term "angiosperms" derives from the two Greek words : angeion meaning "vessels" and sperma meaning "seeds".
2. Angiosperms (flowering plants) are the largest group of plants on earth.
3. Approximately 270,000 known species alive today.
4. Angiosperms include all plants that have flowers and account for approximately 80% of all known living plants.
5. Angiosperms means " covered seeds" have flowers, have fruits with seeds.
Live everywhere- dominants plants in the world.
6. 260,000 species (88% of plant kingdom).
Angiosperms are most successful and advanced plant on earth.
Evolutionary Development of Angiosperms:-
1. Angiosperms evolved during the late Cretaceous period, about 125-100 million years ago.
2. This leaf imprint shows a ficus speciosissiva an Angiosperms that flourished during the Cretaceous period.
3. A large number of pollinating insects also appeared during this same time.
4. Advancements over gymnosperm: angiosperms have flowers- many use pollinators.
5. Fruits and seeds adapted for dispersal.
6. Double fertilization of endosperm in the seed.
Characteristics of Angiosperms
1. Angiosperms have developed flowers and fruits.
2. Flowers serves as the reproductive organs for the plants.
3. Flowers have a wide array of colors, shapes and smells all of the which are for the purpose of attracting pollinators.
1. Roots, stems and leaves.
2. Xylem and phloem.
4. Xylem- conveys water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the shoots.
5. Pholem- transports food made in the leaves to the roots and developing leaves and fruits.
6. They are Heterosporous.
Terminologies:-
a. Androecium- bearing one or more stamens.
b. Gynoecium- bearing one or more carpels.
c. Bisexual (perfect) flower- containing both stamens and carpels.
d. Unisexual (imperfect) flower- having only stamen or carpels.
Distribution of Angiosperms:-
1. One reason for this dominance is the relatively high photosynthetic capacity of their leaves.
2. They occupy every habitat on earth except extreme environment such as the highest mountain tops, the regions immediately surrounding the poles and deepest oceans.
3. They lives as Epiphytes, (i.e. living on other plants).
4. They occur abundantly in-
Shallows of rivers and fresh water lakes.
To a lesser extent, in Salt lakes and in the sea.
Angiosperms life cycle:-
Flower has male and female sex organs.
Flower structure and it's part:-
1. Male sex organs: stamens, composed of anther- organ that produces pollen (male gametophyte).
2. Female sex organs- the carpel.
3. Ovary is the enlarged basal portion of carpel that contains the ovules (females gametophyte).
4. The stigma is the receptive portionof the carpel for pollen grains to adhere.
6. Petals (usually colored) are the inner whorl of leaf-like bracts.
7. Both can have various shaped and colors.
SEEDS:-
Endosperm is stored food tissues for the embryo to grow. Mature ovule becomes the seed coat and fruits.
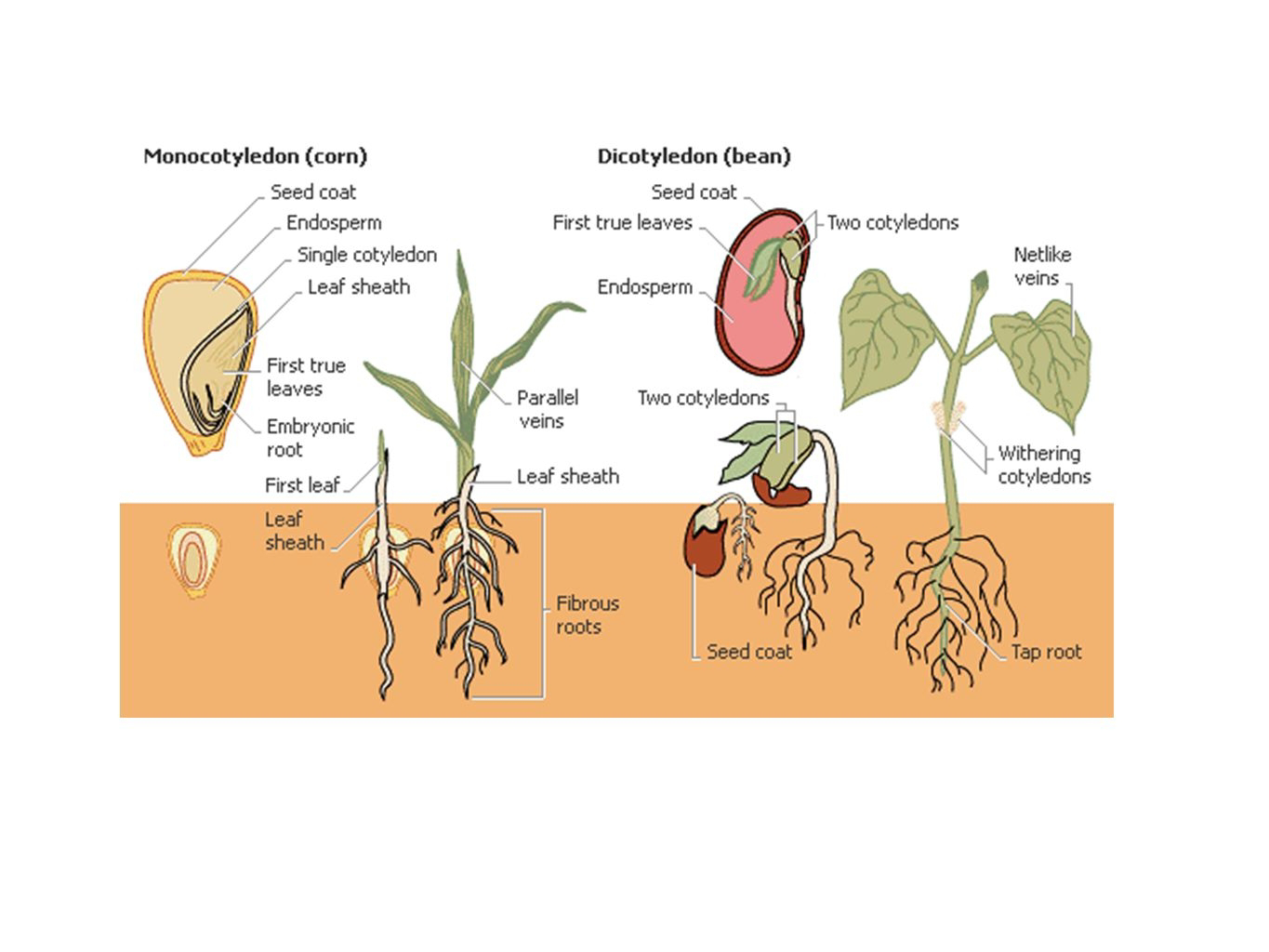
Monocot vs Dicot
1. Angiosperms are divided into monocots and dicots.
2. As the zygote grows into the embryo, the first leaves of the young sporophyte develop and are called as cotyledons (seed leaves).
3. Monocots have one cotyledons (corns, lily etc).
4. Dicots have two cotyledons (beans, oak etc).
Economic Importance of Angiosperms
The flowering plants have a number of uses as food, specifically as grains, sugars, vegetables, fruits, oils, nuts and spices.
In addition, plants and their products serve a number of other need such as dyes, fibres, timber, fuel, medicines, and ornaments.
Thank you🙏











0 comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts. Please let me know.