"Genetic is collective study of heredity and variations".
OR
"Genetics is a field of biology that studies how traits are passed from parents to their offspring".
Genetic term is given by William Bateson in the year 1905.
Heredity- Transformation of genetic character from one generation to another.
Variation- Individual of same species have same differences.
There are two types of Variation
1. Somatic variation- they are non inheritable.
2. Germinal/blastogenic variation- they transfer from one generation to another. i.e. inheritable
a. Continuous (occurs due to crossing over)
b. Discontinuous (occurs due to mutations)
G. J. Mendel is father of genetics. He gave basic principles of genetics in the year 1866.
W. Bateson is father of morden genetics.
Morgan is father of experimental genetics. He did experiments on Drosophila and proposed concept like linkage, sex linkage, crosiing over, criss-cross inheritance, linkage map of Drosophila.
A. Garrod is father of human genetics and Biochemical genetics. He discovered first human metabolic Disorder, i.e. Alkaptonuria ( Balck urine disease). He gave concept of one-mutant gene one-metabolic block.
TERMS OF GENETICS:-
Gene, allele, locus, homologous chromosomes, Dominant, Recessive, homozygous, heterozygous, gamete formation, phenotype, genotype.
Cell
GENE- A gene is the basic physical and functional unit of heredity that controls a particular trait of an organism.
HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOME- At the same locus , same character of gene is present are called homologous chromosomes.
Example- In human 46 chromosomes are present in 23 pairs.
maternal and paternal having same character of gene, at the same location; means both have same gene for eye colour.
LOCUS- Particular location of gene on chromosomes.
ALLELE- An allele is an alternate form of same gene, located on same locus on the homologous chromosomes.
OR
Allele are the gene which is coding for the same character but not for same trait. (Alternate form of gene)
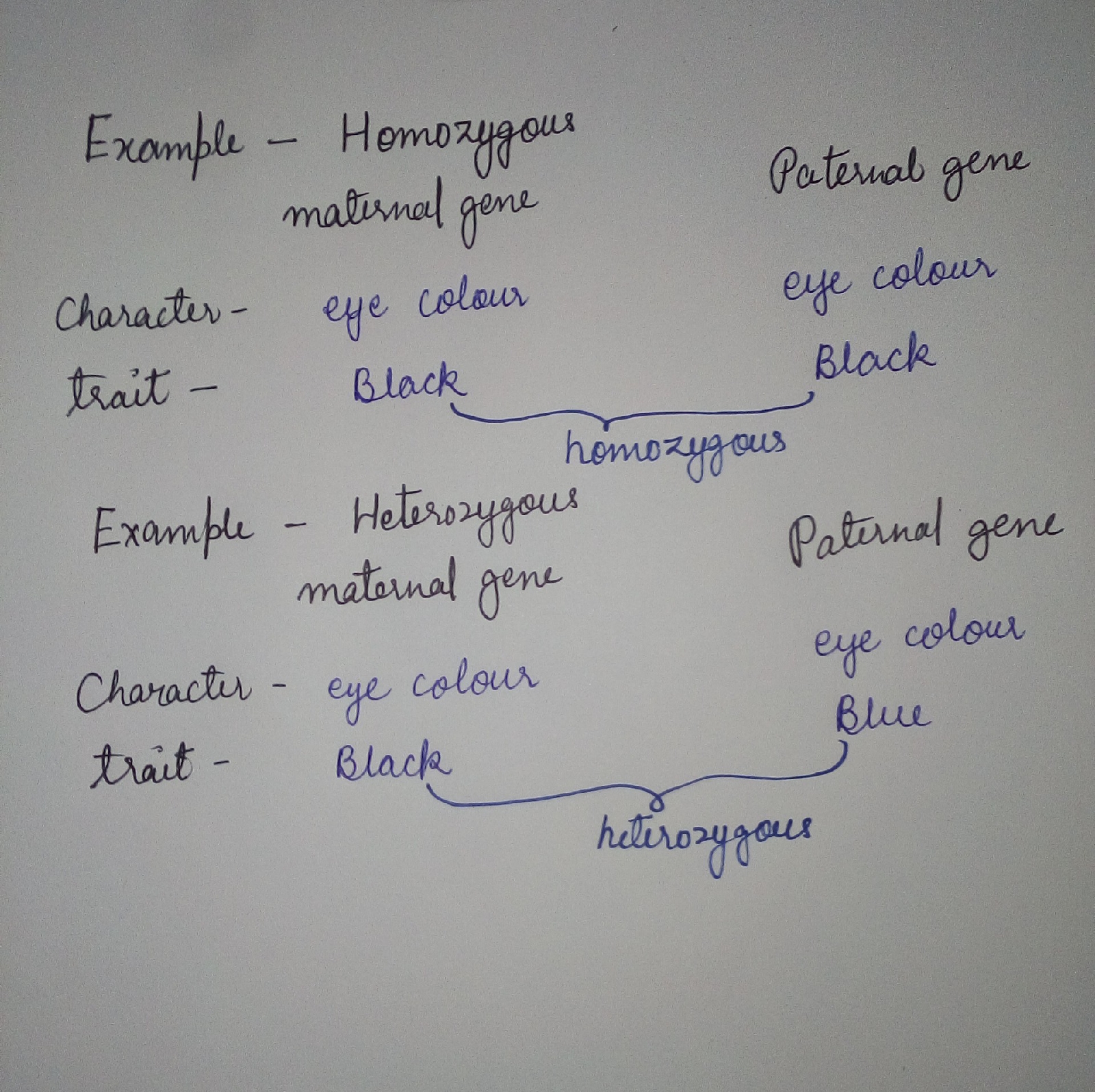
Character- eye colour.
Trait- Blue, black, brown etc.
Alleles were first defined by Gregor Mendel in the law of segregation.
DOMINANT- A genetic trait is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of that gene. A dominant trait is opposed to a Recessive trait which is expressed only when two copies of the gene are present.
RECESSIVE- A recessive gene is a gene whose effects are masked in the presence of a Dominant gene. Every organism that has DNA packed into chromosomes has two alleles, or forms of a gene , for each gene ; one inherited from their mother and one inherited from their father. A Recessive gene is only expressed when an organism has two recessive alleles for that gene.
This is also known as Being homozygous recessive. If an organism has one dominant and one recessive allele, it will show the dominant trait.
HOMOZYGOUS- Homozygous is a word that refers to a particular gene that has identical alleles on both homologous chromosome. It is referred to by two capital letters (XX) for a dominant trait, and two small letters (xx) for a Recessive trait.
HETEROZYGOUS- Gene come in pairs, called alleles and each pair is located in a specific position (locus) on a chromosome. If the two alleles at a locus are identical to eachother, they are Homozygous; if they are different from one another, they are Heterozygous.
GENOTYPE- Genetic makeup.
An organism genotype is the set of gene in its DNA responsible for the particular trait.
PHENOTYPE- physical features/apperance.
An organism phenotype is the physical expression of those gene.
OR
All the observable characteristics of an organism that results from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. Example- colour, shape, size.
GAMETE FORMATION
Gametes are formed through a process of cell division called meiosis. This two-step division process produces four haploid daughter cells.
Haploid cells contain only one set of chromosomes. When the haploid male and female gametes unite in a process called fertilization, they form zygote. The zygote is diploid and contain two sets of chromosomes.
Thank you👍













0 comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts. Please let me know.